Omega-3 Fatty Acids Are Essential, Not Voluntary
The cold hard truth is that omega 3s are not sexy. They don’t give you extreme energy like a pre-workout. They don’t give you skin tearing pumps like a non-stimulant pump powder. You don’t get laser vision like they claim you get from nootropics. They don’t increase your muscle size by 2x like some muscle builders claim they do. The real truth, the important truth is that omega 3s may not do any of those things, but they have been proven via science to improve your overall health.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Explained
In order to fully understand how you can benefit from omega 3 supplementation, it is important to understand what omega 3s are, how much you should be getting and where you can get them from.
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of fat the body cannot make on its own. They are an essential fat, which means they are needed to survive. You can get omega-3 fatty acids from various food sources and supplementation. They’re key to the structure of every cell wall we have. In short, they are essential to a healthy lifestyle.
The three omega-3 fatty acids are Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA), Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA), and Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA).
Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA)
Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA) is one of the main omega-3 fatty acids. Your body cannot produce ALA, so you must get it from food sources such as flaxseed, soybeans and canola oils. Typically plant oils contain ALA as well as nuts and seeds.
ALA can be converted in the body into EPA and DHA, however the conversion rate is extremely low. Therefore, additional food consumption and/or supplementation is required to increase levels of EPA and DHA in the body.
ALA plays important roles in energy production. Other research suggests that ALA may reduce heart disease by helping maintain normal heart rhythm and pumping.
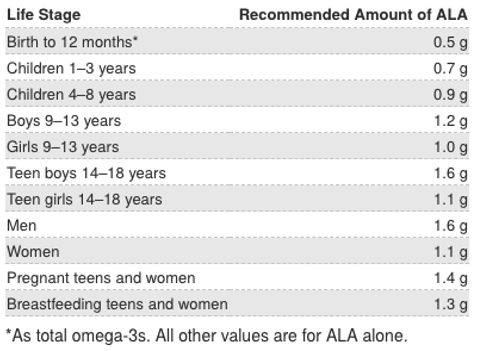
ALA is the only one of the omega-3 fatty acids with a daily recommended dosage. The recommended dosage depends on age and sex.
Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA)
EPA is a popular omega-3 fatty acid. EPA can be sourced from cold-water fatty fish like salmon, tuna, mackerel, sardines, shellfish, and herring. You may also supplement with a fish oil to get an adequate amount of EPA.
EPA has several roles within the human body. According to Mount Sinai, EPA is used to potentially reduce ADHD symptoms, depression, heart disease, rheumatoid arthritis, menopause and more.
Although there are no determined values of recommended EPA amounts, Mount Sinai recommends at least 220mg of EPA per day to meet essential nutrient needs.
Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA)
DHA is the other popular omega-3 fatty acid. According to the National Institute of Health, DHA is an important component of the membranes that surround each cell in your body. DHA levels are especially high in retina, brain, and sperm cells.
DHA can also be found in seafoods such as salmon, tuna, mussels, fish eggs, and more.
DHA plays a major role in cognitive development. A study concluded that twenty-four week supplementation with 900 mg/d DHA improved learning and memory function in age-related cognitive decline patients and is a beneficial supplement that supports cognitive health with aging. DHA also can help with healthy eye sight.
There is no recommended dosage of DHA, but experts say you should be getting around 1,000mg of EPA/DHA combined each day.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids from Foods
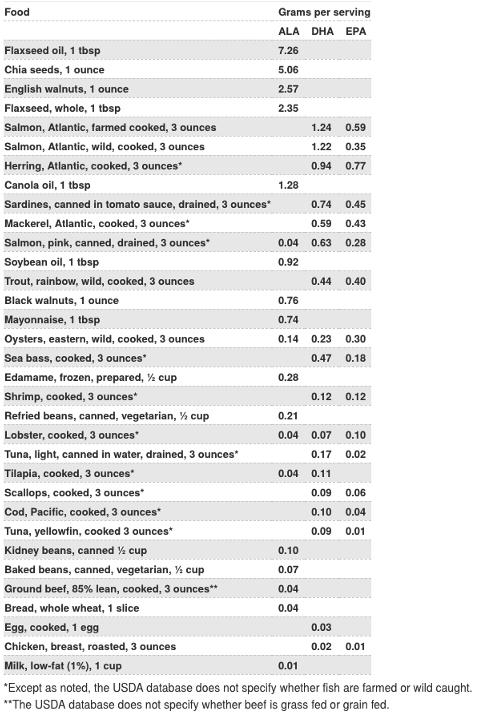 It is important to remember that omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that cannot be produced by the body. You must obtain your omega-3 fatty acids from either a food source or supplementation.
It is important to remember that omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that cannot be produced by the body. You must obtain your omega-3 fatty acids from either a food source or supplementation.
The following foods are great options for getting your omega-3 fatty acids:
- Flax Seeds (ALA)
- Chia Seeds (ALA)
- Salmon (EPA/DHA)
- Tuna (EPA/DHA)
- Walnuts (ALA)
- Soybean (ALA)
- Sardines (EPA/DHA)
It is always recommended that you get the most of your daily intake from food sources. However, if these foods are not readily available then it is best to supplement to obtain your recommended daily intake.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids from Supplements
The market is flooded with various omega-3 supplements. A simple Google search populates about 194,000,000 results. This is overwhelming to an experienced individual and just down-right scary for someone who doesn’t know what they are looking for.
It is important when looking for a quality omega-3 supplement to look for EPA and DHA levels. Do not base your purchase decision on marketing or packaging. Each omega-3 supplement should disclose EPA/DHA on the label. If they do not, then put it back on the shelf.
A reputable brand that we’ve used is Wiley’s Finest. They have a plethora of omega-3 supplements formulated for lifestyle. Whether you’re looking for an option for your children or yourself, they have some thing for everyone. Wiley’s Finest also has omega-3 supplements for those who are pregnant and nursing.
If you’re an adult looking for a premium omega-3 supplement, we recommend Wiley’s Finest Peak Omega-3 Liquid. This product yields 1,400mg EPA and 900mg DHA for a total of 2,300mg of omega-3 fatty acids. This product will give you more than adequate amounts of EPA and DHA you need for healthy functionality.
If you’re looking for something that is more “on-the-go” Wiley’s Finest Peak EPA is in capsule form and provides 750mg EPA and 250mg DHA.
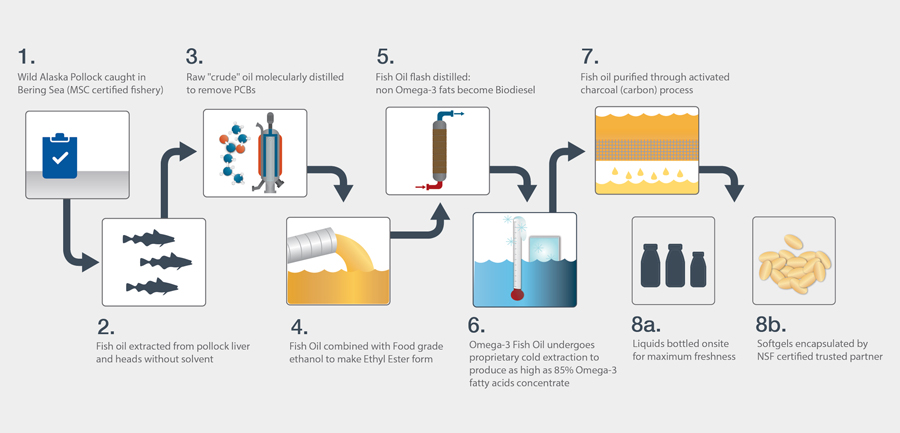
Whatever direction you decide to take on your omega-3 fatty acid supplementation, make sure you buy from a reputable brand that is providing you with adequate amounts of EPA and DHA. It is also important to educate yourself on their process (how they distill their oils).
Wiley’s Finest publishes their process on their website. They also have a sustainability statement as well.
Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids have a lot of benefits. Many of which we already covered above. However, let’s take a closer look at how omega-3 fatty acids may aid in your fitness journey.
Omega-3 and Cardiovascular Support
The most popular and obvious benefit is cardiovascular support. Research shows that getting adequate amounts of omega-3 fatty acids provide protection to the heart by reducing the most common risks associated with the cardiovascular disease including high LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels and factors that contribute to coagulation of blood. Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to significantly reduce the risk for sudden death caused by cardiac arrhythmias and all-cause mortality in patients with known coronary heart disease. EPA and DHA (not ALA) are also used to treat hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol) and hypertension (high blood pressure).
You cannot achieve your fitness goals if your heart stops. This is by-far the most important benefit of omega-3 fatty acids.
Omega-3 and Recovery
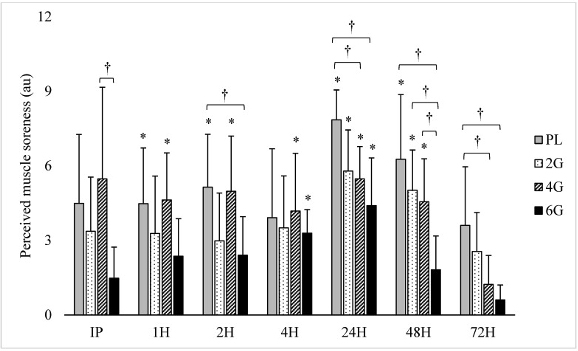 Research suggests that proper intake or supplementation of omega-3 fatty acids can aid in muscle soreness reduction. A study looked at thirty-two college-aged resistance-trained males and their perceived muscle soreness. The results indicated that supplementation with fish oil reduced muscle soreness.
Research suggests that proper intake or supplementation of omega-3 fatty acids can aid in muscle soreness reduction. A study looked at thirty-two college-aged resistance-trained males and their perceived muscle soreness. The results indicated that supplementation with fish oil reduced muscle soreness.
Omega-3 and Endurance
Omega-3 fatty acids may help improve overall endurance. There are few studies in this area, but evidence suggests that since omega-3 fatty acids can act as a vasodialator, it can improve overall endurance. In a study in rats, DHA supplementation led to improvement in endurance exercise capacity and mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle.
In a study with cyclists, supplementation of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids increased performance and VO2 Max.
Omega-3 and Muscle-Building
Research suggests that adequate amounts of omega-3 fatty acids may help build muscle as well as reduce muscle loss. Research suggests that supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids (fish oil) may promote muscle protein synthesis (MPS) and in turn, help grow healthy muscle tissue. Other factors like daily protein intake may also play a part in this.
The other side of muscle-building is preventing muscle loss. One particular area of promise is the potential for omega-3 fatty acids to counteract muscle atrophy from periods of muscle-disuse induced by surgery and subsequent bedrest/inactivity. This would suggest that supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids may help preserve muscle-mass during periods of inactivity.
Omega-3 and Weight Loss
Recent research and studies suggest that supplementing or getting adequate amount of omega-3 fatty acids may improve weight loss. Per an analysis of 21 different studies, it suggested these subjects may benefit from reducing abdominal fat with fish oil supplementation especially when combined with life modification intervention.
Some research suggests that supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids may suppress appetite in obese individuals. Other research suggests that a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids showed a positive correlation between omega-3 fatty acids and appetite; the group that ate omega-3 rich foods felt less hungry after a while.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Conclusion
There are over 40,000 research papers and 50 years of research that show EPA and DHA have positive health benefits on cardiovascular health, mental health and joint support. However, more studies should be conducted to determine the correlation between the hypertrophy and recovery benefits listed here and the increase of omega-3 fatty acids, early research seems positive.
Use code INFORMANT to save 10%









