Laxogenin (5a-hydroxy laxogenin)
Laxogenin, also known as 5a-hydroxy laxogenin, is a plant-based ingredient used in many muscle-building supplements. It belongs to a class of plant hormones called brassinosteroids, which have a similar structure to animal steroid hormones. Supplementing with Laxogenin may lead to leaner body composition through increased muscle mass from increased muscle protein synthesis and a reduction in body fat by regulating cortisol levels. It also may lead to increase strength and power outputs, as well as increased athletic performance.
Uses of Laxogenin
Laxogenin is an ingredient derived from plants, the underground stems of the Asian plant Smilax sieboldii contain approximately 0.06% Laxogenin and are its main natural source, that is typically found in muscle-building supplements. Brassinosteroids, the plant hormone family Laxogenin belongs too, has been shown to have anabolic effects that lead to increased power output, increased muscle mass and leaner body composition. Laxogenin has also been shown to reduce cortisol levels and increase muscle protein synthesis by 200%.
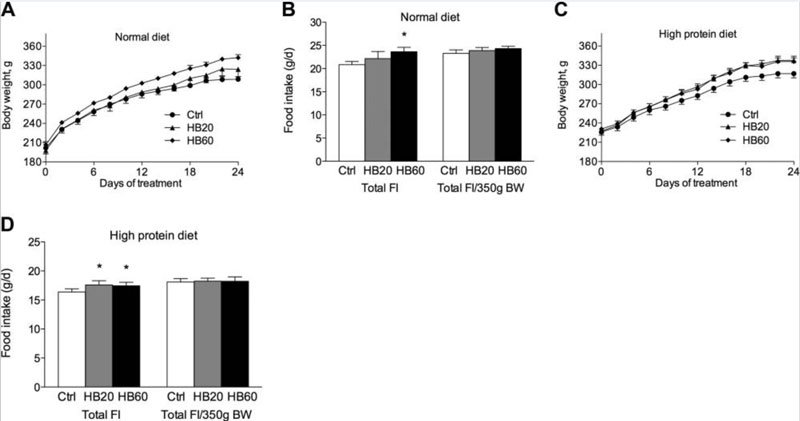
Per a study conducted on rodents, Laxogenin (brassinosteroids) was shown to stimulate protein synthesis and inhibit protein degradation, which lead to increased food intake, body weight gain, lean body mass, and gastrocnemius muscle mass as compared with vehicle-treated controls. Rodents were given either 20mg or 60mg (or none) of Laxogenin (brassinosteroids) for 24-days consistently. Measures were taken before and after the 24-days. The study did look at a normal diet (23.9% protein) vs. a high protein diet (39.4% protein).
Regarding protein synthesis, the rebuilding of muscle tissue, one study indicated that Laxogenin can increase protein synthesis by up to 200%. More studies need to be conducted to validate these claims.
The main use of Laxogenin (Brassinosteroids) is for is for the anabolic properties (i.e. lean body mass gains). Anabolic is defined as any state in which nitrogen is differentially retained in lean body mass, either through stimulation of protein synthesis and/or decreased breakdown of protein anywhere in the body. Rodents were fed a normal diet and given 20mg or 60mg per day over 24-days. By the end of the study, the total body weight gain relative to initial body weight in rats treated with 20mg or 60mg was 18.3% and 26.8% more compared with the control group. Although a slight increase in food intake was observed for the 20mg group, but when adjusted for for body weight, food intake did not differ among the groups.
Body composition was also measured as part of the study. Body composition was measured via DEXA scan, one of the most reliable body composition measurement systems. Lean body mass was measured in both the 20mg and 60mg group. The 20mg group resulted in a 7% increase while the 60mg group resulted in a 14.2% increase in lean body mass. Fat mass was reduced in both the 20mg and 60mg group. The 20mg group had a reduction in fat mass by 3.9% while the 60mg group had a reduction in fat mass by 4.9%.
The same measurements were conducted with a high protein diet (39.4% protein). The control group (no Laxogenin) actually consumed less food on a high protein diet vs. the control group on the normal diet, and gained less weight. After the 24-day study period, it was determined that the 20mg group gained slightly more weight than the normal diet 20mg group, however no statistical differences were noted between either the 20mg or 60mg on the high protein vs. the normal protein diet.
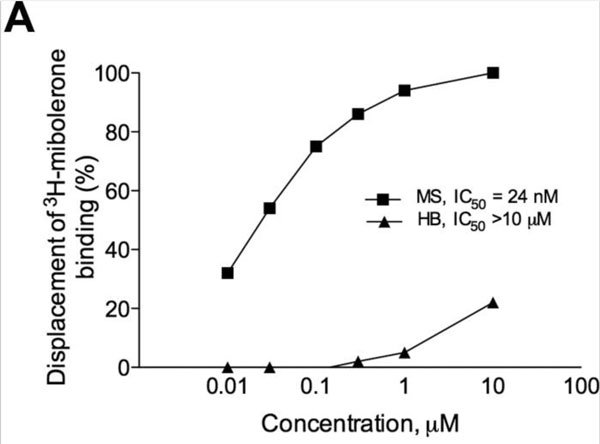
Laxogenin is also non-hormonal. This means it does not bind to an androgen receptor. It does not act via hormonal pathways in the human body and does not interfere with natural hormone production. In particular, it has no effect on the hypothalamus-pituitary-testicular-axis or estrogen levels, nor does it suppress luteinizing hormone like many popular anabolic steroids. Furthermore it does not put excess strain on the liver. This study looked at methandrostenolone compared to brassinosteroids (Laxogenin). The results were that methandrostenolone produced specific binding to the androgen receptor while Brassinosteroids (Laxogenin) did not. This means a PCT is not required while using Laxogenin.
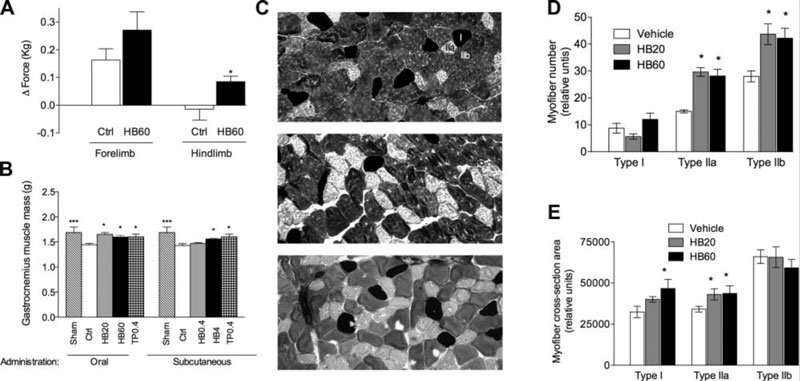
Brassinosteroids like Laxogenin also showed to increase in grip strength in both lower extremities and upper extremities vs. control group. This study was conducted over 10-days with a control group vs. a 60mg dosage of Brassinosteroids. The results showed that Brassinosteroids can improve physical fitness of untrained healthy rats, as evident from a 6.7% increase in lower extremity strength.
Brassinosteroids (Laxogenin family) was also shown to increase muscle mass through the repairing and rebuilding of Type IIa and Type IIb muscle fibers. The study looked at androgen deprivation. Androgen deprivation caused significant decrease in the gastrocnemius muscle mass to 85.8%. Then the subjects used 20mg or 60mg of Brassinosteroids (Laxogenin family) for 10-days. The results showed that oral supplementation with Brassinosteroids increased gastrocnemius muscle mass by 13.8% (20mg) and 10.3% (60mg) groups.
Laxogenin is also believed to enhance muscle recovery and growth by inhibiting the stress hormone cortisol. Excessive cortisol levels can make it almost impossible to gain muscle, not to mention strength. Per the patent application, Laxogenin:
Adaptogens are reputed to have an anti-stress effect mainly towards stresses of a non-infectious agent. In this aspect adaptogens differ from the spirostanic spirostane and spirostene “addaptogens” (from “additive” and “adaptogens”) or “adaptogenins” (after “adaptogen” and “laxogenin”) of the current invention, which have broad-spectrum immuno-enhancing and immuno-stimulating properties that are also useful to restore homeostasis, normalize functions, enhance protein synthesis and improve numerous other biochemical and physiological functions by -up-regulation and down-regulation of genes and biochemical systems as needed. The general purpose of adaptogens is the reduction of stress reactions in the alarm phase, thereby avoiding the exhaustion stage and providing a certain protection against stress and rebuilding the body after stress or fatigue. Adaptogens or adaptogenins of the current invention also provide protection prior to and during the alarm phase and exhaustion stage as well as providing numerous benefits after stress or fatigue.
Overall, there are many uses for Laxogenin, with the main ones being increased muscle protein synthesis and regulation of cortisol levels leading to lean body composition, muscle mass gains, lower body fat, strength and power output and increased athletic performance.
NOTES:
- The studies referenced above were conducted on Brassinosteroids, the family of plants that Laxogenin is derived from
- Limited studies have been conducted on Laxogenin. Human studies should be conducted to validate the above information.
- Recent studies conducted on OTC Laxogenin products indicated that several of those product did not actually contain 5α-hydroxy Laxogenin
Interactions with Laxogenin
Laxogenin is typically used as a stand-alone product. Ingredients such as AstraGin and BioPerine can be used to aid in absorption. Other ingredients such as VASO6 have also been used with Laxogenin.
Side Effects of Laxogenin
Per studies, Laxogenin triggers an anabolic response with minimal or no androgenic side effects.
Recommended Laxogenin Dosage
Although there is not a recommenced clinical dosage of Laxogenin, we recommend 100mg-200mg of Laxogein per day for optimal results.
A PCT is NOT required with Laxogenin due to it being non-hormonal.
Recommended Supplements Featuring Laxogenin
The following products contain Laxogenin at the recommended dosage, and are recommended supplements for Fitness Informant: